Blog Posts
5 Algorithms that Demonstrate Artificial Intelligence Bias
It is an unfortunate fact of our society that human beings are inherently biased. This may happen consciously where humans are biased towards racial minorities, religions, genders, or nationalities and this may even happen unconsciously where biases develop as a result of society, family, and social conditioning since birth. Whatever the reason, biases do exist in humans and now they are also passed into the artificial intelligence systems created by humans.

These biases can be passed into Artificial Intelligence Bias in AI systems when they are trained on data that includes human biases, historical inequalities, or different metrics of judgement based on gender, race, nationality, sexual orientation, etc. of humans. For example, Amazon found out that their AI recruiting algorithm was biased against women. This algorithm was based on the number of resumes submitted over the past 10 years and the candidates hired. And since most of the candidates were men, so the algorithm also favored men over women. As you can see from this example, biases in Artificial Intelligence causes a lot of damage. This bias hurts the chances of the biased group to participate fully in the world and provide equal benefits to the economy. And while it hurts the groups that the algorithm is biased against, it also hurts the trust of humans in the artificial intelligence algorithms to work without bias. It reduces the chances of Artificial Intelligence being used in all aspects of business and industry as this produces mistrust and the fear that people may be discriminated against. So technical industries that produce these artificial intelligence algorithms need to ensure that their algorithms are bias-free before releasing them in the market. Companies can do this by encouraging research on Artificial Intelligence Bias to eradicate bias in the future. But before this can happen, we also need to know the examples where Artificial Intelligence Bias was demonstrated by different algorithms. So let’s see them so that we can understand what algorithms should not do in the coming times.
Which algorithms demonstrate Artificial Intelligence Bias?
These are some algorithms that have demonstrated Artificial Intelligence Bias. Notably, this bias is always demonstrated against the minorities in a group, such as Black people, Asian people, women, etc.
1. COMPAS Algorithm biased against black people
COMPAS, which stands for Correctional Offender Management Profiling for Alternative Sanctions is an artificial intelligence algorithm created by Northpointe and used in the USA to predict which criminals are more likely to re-offend in the future. Based on these forecasts, judges make decisions about the future of these criminals ranging from heir jail sentences to the bail amounts for release. However, ProPublica, a Pulitzer Prize-winning nonprofit news organization found that COMPAS was biased. Black criminals were judged to be much more likely to re-commit crimes in the future than they committed. On the other hand, white criminals were judged less risky than they were by COMPAS. Even for violent crimes, black criminals were misclassified as more dangerous almost double the time as compared to the white criminals. This discovery in COMPAS proved that it had somehow learned the inherent bias that is frequent in humans, which is, black people commit many more crimes than white people on average and more likely to commit crimes in the future as well.
2. PredPol Algorithm biased against minorities
PredPol or predictive policing is an artificial intelligence algorithm that aims to predict where crimes will occur in the future based on the crime data collected by the police such as the arrest counts, number of police calls in a place, etc. This algorithm is already used by the USA police departments in California, Florida, Maryland, etc. and it aims to reduce the human bias in the police department by leaving the crime prediction to artificial intelligence. However, researchers in the USA discovered that PredPol itself was biased and it repeatedly sent police officers to particular neighborhoods that contained a large number of racial minorities regardless of how much crime happened in the area. This was because of a feedback loop in PredPol wherein the algorithm predicted more crimes in regions where more police reports were made. However, it could be that more police reports were made in these regions because the police concentration was higher in these regions, maybe due to the existing human bias. This also resulted in ina bias in the algorithm which sent more police to these regions as a result.
3. Amazon’s Recruiting Engine biased against women
The Amazon recruiting engine is an artificial intelligence algorithm that was created to analyze the resumes of job applicants applying to Amazon and decide which ones would be called for further interviews and selection. This algorithm was an attempt by Amazon to mechanize their hunt for talented individuals and remove the inherent human bias that is present in all human recruiters. However, the Amazon algorithm turned out to be biased against women in the recruitment process. This may have occurred as the recruiting algorithm was trained to analyze the candidates’ resume by studying Amazon’s response to the resumes that were submitted in the past 10 years. However, the human recruiters who analyzed these resumes in the past were mostly men with an inherent bias against women candidates that were passed on to the AI algorithm. When Amazon studies the algorithm, they found that it automatically handicapped the resumes that contained words like “women” and also automatically downgraded the graduates of two all-women colleges. Therefore Amazon finally discarded the algorithm and didn’t use it to evaluate candidates for recruitment.
4. Google Photos Algorithm biased against black people
Google Photos has a labeling feature that adds a label to a photo corresponding to whatever is shown in the picture. This is done by a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) that was trained on millions of images in supervised learning and then it uses image recognition to tag the photos. However, this Google algorithm was found to be racist when it labeled the photos of a black software developer and his friend as gorillas. Google claimed that they were appalled and genuinely sorry for this mistake and promised they would correct it in the future. However, all Google had done until 2 years later was removing gorillas and other types of monkeys from Convolutional Neural Network’s vocabulary so that it would not identify any photo as such. Google Photos displayed “no results” for all search terms relating to monkeys such as the gorilla, chimp, chimpanzee, etc. However, this is only a temporary solution as it does not solve the underlying problem. Image labeling technology is still not perfect and even the most complex algorithms are only dependent on their training with no way to identify corner cases in real life.
5. IDEMIA’S Facial Recognition Algorithm biased against black women
IDEMIA’S is a company that creates facial recognition algorithms used by the police in the USA, Australia, France, etc. Around 30 million mugshots are analyzed using this facial recognition system in the USA to check if anybody is a criminal or a danger to society. However, the National Institute of Standards and Technology checked the algorithm and found that it made significant mistakes in identifying back women as compared to white women or even both black and white men. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology, Idemia’s algorithms falsely matched a white woman’s face at a rate of one in 10, 000 whereas it falsely matched a black woman’s face at a rate of one in 1, 000. This is 10 times more false matches in the case of black women which is a lot! In general, facial recognition algorithms are considered acceptable if their false match rate is one in 10, 000 while the false match rate found for black women was much higher. Idemia claims that the algorithms tested by NIST have not been released commercially and that their algorithms are getting better at identifying different races at different rates as there are physical differences involved in races.
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/5-algorithms-that-demonstrate-artificial-intelligence-bias/
Alan Turing and his enduring legacy
Alan Turing was born in London in 1912 just two years before the First World War. Growing up in the aftermath of brutal international conflict, Turing’s parents were keen to ensure that their son was able to thrive within education.

Early life
His passion for learning became clear when at the age of 13, the 1926 General Strike prevented Alan from attending his first day of school. Determined not to miss it, Alan Turing cycled 60 miles on his bike unaccompanied, stopping overnight at an inn and attending school the next day.
Achievements and Hardships
It became clear from an early age that Alan Turing was a maths prodigy, and over the course of his life and career Turing pioneered mathematics and computer science, changing the way we see and understand the world. From altering the course of history by breaking the Enigma code at Bletchley Park during the Second World War, through to applying his practical war-time experiences to design the principles of which underlie modern computers, Alan Turing’s legacy has shaped the lives of millions of people.
However, Alan Turing faced much hardship during his life due to his sexuality. During Turing’s life, homosexuality was a criminal offence and Turing was convicted in 1952 of “Gross Indecency”. Alan Turing was faced with an impossibly cruel choice of imprisonment, or probation on the condition he underwent chemical castration. Turing died from suicide two years later.
More than a century since the birth of mathematician Alan Turing, much has changed within the social, political and cultural landscape of the UK. One of the defining markers of change has been the LGBT+ liberation movement, which began in the 1970s and campaigned for equal rights for the gay community.
Thanks to the efforts of activists, historians and politicians, Turing’s legacy has not been forgotten. In 2013,HM Queen Elizabeth II signed a pardon for Turing’s conviction with immediate effect. Since then, the Alan Turing Law has gone on to secure pardons for 75,000 other men and women convicted of similar crimes.
Source: https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2021/02/19/lgbt-history-month-alan-turing-and-his-enduring-legacy/
Tips: accessibility for users with low-vision
1. Relative Font Sizes
Use relative font sizes expressed in percentages or ems, rather than absolute font sizes expressed in points or pixels. This practice allows users to make the text larger or smaller as desired—an important feature for users with low vision. See Tips for Computer Users With Low Vision for more details.
2. Provide Alternative Text for Images
It is absolutely necessary to provide text equivalents for all meaningful graphics. If the graphic includes text, be sure that the alternative text (often referred to as an "alt tag") supplies all of the words.
Example:
<img src="graphic.gif" alt="Acme - supplying widgets since 1945" width="50" height="20">
That said, providing "alt" text for spacers or placeholding graphics subjects the speech user to meaningless information. Spacers or graphics used only for positioning should be labeled with alt=" " (quote, space, quote). Note that you should never completely omit the alt tag, even for placeholding graphics. This omission subjects the speech user to hearing the file name of the image.
If you are in doubt as to whether or not to describe an image with an alt tag, do it.
3. Name Links Carefully
Users often move through a page by tabbing from link to link. Never use "Click here" or "Learn More" as the text for your links. "Download SuperSoftware 4.8" is self-explanatory.
4. Explicitly State Information
Do not use indentation or color alone, for example, to convey meaning.
Example:
Indicating required fields in a form by making them bold is bad. Indicating required fields by using a phrase such as "required" is ok.
5. Provide Skip Links
Skip links allow the speech software or braille user to bypass information that is repeated on every page, such as navigation bars. Speech and braille users generally read the page from top to bottom, and consequently are subjected to repeated information before reaching the heart of the page. Skip links allow these users to jump past the repetitive navigation links to get to the main content on the page.
To implement skip links, place a link before the repeated information as follows:
<a href="#content"><img src="empty.gif" height="15" border="0" alt="Skip Main Navigation" width="5"></a>
and place an anchor at the beginning of unique copy:
<a name="content"></a>
The image can be transparent, so that the visual display is not affected, but speech and braille users can hear the alt tag reading "skip main navigation".
It is also possible to use a text link that literally says <a href="#content">skip main navigation</a>, if you prefer. We do not recommend using an "invisible" text link, like a single space or underscore. That technique relies on the link's title to provide accessibility, and not all screen readers provide the link title to the user.
Source: https://www.afb.org/consulting/afb-accessibility-resources/tips-and-tricks
The Importance of Web Accessibility for Everyone
Some people believe that web accessibility is not a concern for everyone and that it only needs to be taken into account for those with disabilities. However, the truth of the matter is that by definition, web accessibility benefits everyone. Web accessibility means that there are no restrictions on who can access information on the internet equally, despite age or disability.
Web accessibility stems from our need to work together in an international world where people have different backgrounds and language skills- thus making it essential to take into consideration how these differences may affect their experience while using your site.
Web accessibility benefits everyone because it allows people with disabilities to access information much more easily. Right now, if you were to try and use Facebook (which is one of the most popular websites in the world) with a screen reader (for example, JAWS or NVDA), you would not be able to complete your goal. If you were to try and use more complicated websites like Gmail or Pinterest, you would not be able to simply understand how to navigate through the site (literally at all). With web accessibility for people with disabilities, they will be able to access information on your website easily and effectively. Not only that, but it benefits everyone by making their online experience easier as more sites become more accessible to people with disabilities.
Web Accessibility Benefits Everyone
By the very definition of the word "accessibility" web accessibility means that everyone ought to be able to access information on the Internet equally. There are no restrictions based on age, physical or mental abilities, language skills, etc. The whole idea stems from the fact that this is an international world and people need to work together for the common good of mankind.
However, you may be wondering whether this is really a valid concern. My answer to that would be "yes". Here's my story: I am in my early 20s and I have never been totally able-bodied. Although it has not hindered me from doing anything major, the fact remains that at some point or another my physical abilities have been a hindrance to me. Of course, it is only a minor inconvenience and I have no reason to complain about it - but the point I am trying to make is that even if you are healthy as a fiddle, you still should consider the needs of those who may not be. Especially considering that currently there are more people on the Internet than the total population of the planet, which is over 7 billion people.
Web accessibility means that there are no restrictions on who can access information on the internet equally, despite age or disability. It does not matter what age you are or what your physical or cognitive disabilities are, you should be able to access the world wide web just like anyone else. This way, everyone can share ideas and communicate with one another about the same things. It is important that all people in this world have equal opportunity to learn, explore and educate themselves.

Now that we've defined what web accessibility is, let's look at some methods for making websites and applications more accessible. The following are the most common ways to ensure a website or application is accessible:
- Provide meta-browser information: Ensure that your product provides user agents and other browser information so users of all browsers can access your site.
- Make use of WAI-ARIA: This provides a more advanced solution to making your site accessible to all users who may need assistive technologies such as screen readers. There are more solutions like this which you can explore for yourself on Google or other search engines.
- Ensure that your product's code is compliant with the WCAG 2.0 guidelines: When you use your product's code on your website, ensure that it comply with the WCAG 2.0 guidelines. This will help users to access all of your content and functionalities without any problems or restrictions.
- Present alternatives for multimedia objects: If you use an audio file as part of your site's design (for example, for sound effects), ensure that the file is accompanied with an alternative text version so users can know what they are not hearing.
- Use clear language: If you use technical or specific language in your product's design, ensure that there are also alternative ways of explaining the same thing in simpler terms. This way, you can accommodate all users who may not understand the technical jargon.
- Do not restrict your content: Ensure that you do not restrict any of your products' content so users can access them if they want to skip certain parts, go back, or just simply read through everything in order
- Make JavaScript/AJAX alternatives available: If your product uses JavaScript/AJAX, ensure that there are also alternative ways of interacting with your product, such as a link to a printable version or an email address which users can use to ask questions if they have any problems.
- Provide captions and subtitles: If you include multimedia content in your site design (such as video), provide text transcriptions or captions so users with hearing impairments can understand what they are seeing.
- Use keyboard-only controls: If you include interactive features in your design (such as games), ensure that users can access them by using just the keyboard without having to use a mouse
- Ensure that your product provides sufficient contrast: This is very important and sometimes forgotten because it appears that people are only supposed to be viewing your product on a computer screen. The thing that you should always remember is that everyone will be accessing your site in all sorts of lighting conditions, so it is important that your website provides sufficient contrast to remain visible under all circumstances.
- Obfuscate personal and contact information: This has become increasingly common for some websites. If you wish to provide a number for people to call or an email address to contact, make sure that these numbers and/or addresses cannot be used by the public to track down and find more information about your personal or company information.
- Make sure that your product is compatible across browsers: Ensure that your design works in different browsers so all users can access it.
- Use proper grammar and spelling: Ensure that your product is written properly in English or whatever language you use so users do not have to guess what your message means. This is also useful when people translate your product for other markets, such as Japan.
- Mark up lists and tables: If you use lists or tables in your design, make sure that they are properly marked up so users do not accidentally skip over some of your information.
- Ensure that all content is available in HTML: If you plan on displaying something as part of your product's design (for example, a full banner ad), make sure that there is also an HTML version which the user can access by clicking a link so it can be skipped and they can easily access the information that they want.
- Avoid using audio as warning: If you use some kind of tone or sound to indicate that something is wrong with your design, ensure that there is some other way of letting users know about this problem (such as a red flashing screen which appears for a few seconds).
- Make it easy for users to contact you: If your website includes a link or a button that users can click on to email you, make sure that this feature is readily available and its purpose obvious. Try not to make people search for it as many may not be able to find where the information they need is located.
- Ensure that your product is accessible by all devices: This refers to any computer, tablet, or phone which users may be using. It is important that your website will look the same regardless of what device it is viewed on.
The main reason why web accessibility is so important is because it benefits everyone. Everyone should be able to access information on the Internet equally, whether or not they are using assistive technology. The design of websites should always be universal and focus on the user's needs rather than technological limitations (which may vary from user to user). Web accessibility is the international language of the Internet as it focuses on everyone coming together for a common goal.
Source: https://www.enginess.io/insights/The-Importance-of-Web-Accessibility-for-Everyone
how to insert images using Markdown
Images can be added to any markdown page using the following markdown syntax:

Example:

The result is this:

You can add any image you want. Images can be hosted anywhere on the internet, they will be displayed on the left side of your page.
Remember to add the alt text! It is important to do that, in order to optimize accessibility :D
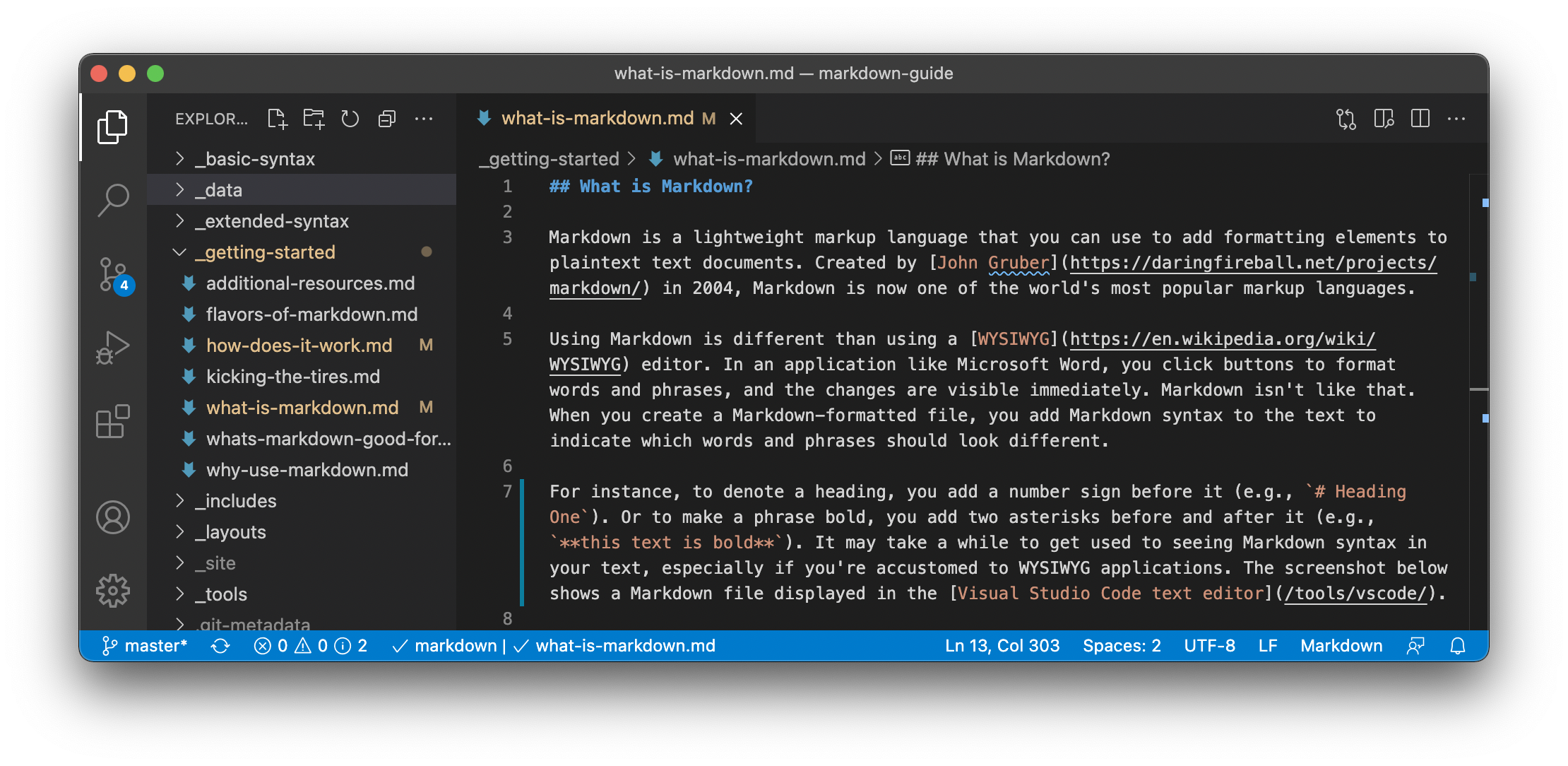
what is Markdown?
Markdown is a lightweight markup language that you can use to add formatting elements to plaintext text documents. Created by John Gruber in 2004, Markdown is now one of the world’s most popular markup languages.
Using Markdown is different than using a WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editor. In an application like Microsoft Word, you click buttons to format words and phrases, and the changes are visible immediately. Markdown isn’t like that. When you create a Markdown-formatted file, you add Markdown syntax to the text to indicate which words and phrases should look different.
For example, to denote a heading, you add a number sign before it. For example:
This is a subtitle
Or to make a phrase bold, you add two asterisks before and after it. For example, this text is bold.
Or to make a phrase italic, you add one asterisk before and after it. For example, this text is italicized.
It may take a while to get used to seeing Markdown syntax in your text, especially if you’re accustomed to WYSIWYG applications. The screenshot below shows a Markdown file displayed in the Visual Studio Code text editor:
That's it for now!
© n-o-t
2023

